Research | Why multiple sites hosted on a shared hosting account can lead to infection of all sites?
Here is the article that cover a real big problem for today, about the shared hosting industry. Security vendors for today are trying to clarify shared hosting aspects to the community, in terms of website security. So here is our contribution in bringing this issue to the community.
What is hosting anyway?
Hosting is a service that allows individuals and businesses to put any website on the Internet for others to see. The websites reside on special computers called “servers”. When someone wants to see your website on the Internet, all they have to do is type your website address into their browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.). Their computer then connects to the server where the website is located, and they can see your website through their browser.
Here’s an example to help you understand: you need to live somewhere (just like a website needs to be placed somewhere), and in this case, your home represents your website’s server. In order for people to find your apartment, they need to know your street address, just like visitors to your website need to know your website’s web address.
How to explain term Shared and term Hosting in one word.
Sharing is caring – simple as that. Shared means that we have situation where many websites are on the same server. Those websites are sharing one sever – the space and resources of the server and each person has access to only a small part of the shared server.
This is a similar situation where you live in your apartment in a building with many other people and you can maybe share the water, electricity and gas of the building with all other people in the same building, but you only pay for what you have used.
Why is Sharing so interesting?
For many people Sharing is the first hosting option, mainly for the following reasons:
- price because usually it is the cheapest solution if you want to put your website on the internet;
- readiness to use because hosting tools you need are already installed and ready to use;
- tech-savvy knowledge don’t needed to use WP Engine/ Kinsta/ Managed WP Hosting;
- high-quality shared hosting usually has fast and competent 24/7/365 support in case you have any problems with the hosting;
Shared hosting disadvantages.
Nevertheless, there are also disadvantages to using shared hosting that we all need to know when choosing this shared hosting for our websites:
- Security concerns: your server “neighbors” may not take the same security measures you do, and if they get hacked, the entire server, including your website. Your website is only as secure as the site with the weakest security measures on the same server.
- Speed issues: because you share your server resources, speed can vary greatly depending on how the other sites use them (if they use more of the server’s memory or CPU processor than allowed);
- Restricted access to settings: restricted access to some advanced server settings: you may not be able to access some advanced servers’ settings;
Although the main responsibility for the security of the server lies with the hosting companies, the owners of the websites are also responsible for maintaining their websites regularly to keep them secure.
Shared Hosting Setup.
Many shared hostings have a similar general setup, typically using cPanel/Plesk: tools for the website owners to manage their account for web hosting with maximum efficiency. Multiple users share a single server to have their own website with their cPanel/Plesk tool.
In this situation, the cPanel/Plesk acts as a virtual landlord of our “apartment building” (personal hosting account) and takes care of it.
Certain hosting companies do not limit the number of websites you can have on your shared hosting account, but they do limit shared hosting usage in the following hosting areas:
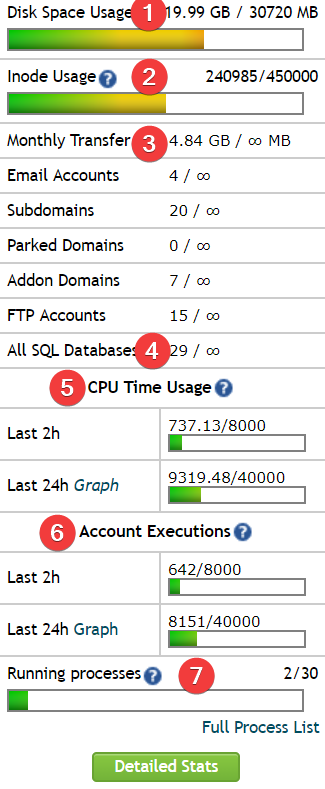
- 1. Disk Space Usage: how much space of shared hosting is available for you (e.g., 30 GB of space)
- 2. Inode Usage: how many files and folders you can have in your hosting account (e.g. 450.000 files and folders)
- 3. Monthly Transfer: how much traffic you can have over a month (e.g. 30 GB)
- 4. All SQL Databases: how many databases you can create (e.g. 30 databases). Typically, 1 WordPress website requires 1 database.
- 5. CPU Time Usage: the amount of CPU time in seconds that all of your websites can consume in the last 2/24h (e.g., 8.000/40.000 CPU seconds)
- 6. Account Executions: the amount of all programs executed in the last 2/24h (e.g. 8.000/40.000 programs)
- 7. Running processes: the total number of currently running processes for your hosting account (e.g. 30 processes)
One well-known example of shared hosting is SiteGround.
How many accounts can exist on the one server?
This mainly depends on the particular shared hosting decision, how many accounts they will put on a particular server to maintain the normal function of the server while maximizing the profit.
Hosting providers usually use the following: the average number of requests from websites per second (the amount they believe their server can handle) divided by the number of shared hosting customers to fully reach the server’s limit.
Multiple websites within one Shared Hosting account.
It is not uncommon for website owners to use one hosting account for multiple websites if their shared hosting provider allows it. Usually, between 2-10 websites are allowed at the lowest rates, which mainly depends on the hosting company used and the shared hosting package chosen.
To better understand the concept of multiple websites within one Shared Hosting account, try to imagine a situation where you live in an apartment along with some subtenants that you let in. It is still your apartment, but you also rent it out to some other people.
If you have situation where shared hosting allows multiple websites, then each of the websites can be a separate WordPress website and show completely different content. However, all of these websites can be managed under one shared hosting account using your cPanel/Plesk tool.
Security risks associated with multiple websites within one Shared Hosting account.
The biggest security risk with shared hosting is when you add multiple websites under the same hosting account.
This is because some shared hostings allow you to access all of your websites with the same FTP account. In case of an infection on one of these websites, all the other websites can easily get infected as well.
Multiple websites are installed in separate folders within the root/main directory of your shared hosting account. This means that if a hacker gets into your shared hosting account, he can access all these folders/websites and all your websites can be compromised at once.
We know exactly how viruses work: they just spread. The same goes for website malware: malware duplicates itself and injects itself in the places you rarely check.
You can only reduce the risk of multiple websites on shared hosting being compromised if you regularly update, monitor, and secure all of your websites, and use strong passwords for the shared hosting account and all of the websites on it. You also need to implement very strong security protection with WAF (Web Application Firewall) like Virusdie. Unfortunately, since these activities require a lot of time and money, not many companies do this.
Stories and Tales.
a). It is commonly believed that hackers can move between two shared accounts – this is the so-called cross-site contamination incident, i.e. when a website in one shared hosting account infects websites in another shared hosting account on the same server.
This usually doesn’t happen, mainly because there is a good layer of security between accounts on the server: strong account isolation and good server configurations. Most web hosting companies make sure that this part of security is well protected, because they are aware of the possible consequences for their customers and their company if something goes wrong: a single insecurity on one website can put all websites at risk.
b). Even if a bad website resides on a server with the same IP, this will not affect the SEO of that website.
Potential impact of shared hosting between accounts.
a). If a website on another account on the same server is affected by hacking/DDoS attacks, then your website is also affected. This also happens if you are using a cloud/web firewall.
b). Hackers often use a hacked website to send spam emails. Email servers like GMail, Hotmail, Outlook etc. blacklist hacked servers when they receive such spam emails from them. Therefore, a hacked website on another shared hosting account will cause your emails to be blocked as well.
Using a third-party email service like MailChimp, Sendgrid, etc. can help in such situations.
c). A hacked website on a shared hosting account can overload the entire server, slowing down your own website on another account.
SUMMARY
With a shared hosting account, you can put many websites on the same hosting account and host many websites for a small price. This is often used by many web agencies to get all of their clients online without paying large sums of money. These websites are typically presented in sub-folders or sub-domains.
However, “a chain is only as strong as its weakest link”: a single bad plugin or weak password could be enough for hackers to get into one website and then all the other websites on the same hosting account.
When hackers get into a website, they are out to do as much damage as possible. They will infect all the files they can see. If the website was isolated, the damage would be limited to just that one website.
However, since we can access another website from the infected website, the hacker runs amok and infects everything.
Whenever a website is hacked, shared hosting locks down the entire hosting account, not just that one website.
Clean up one than scan and clean up all, because if you clean up only one website, the hacker will use the infection (backdoor) to reinfect another website. All websites must be cleaned up quickly or the hacker will be one step ahead of us.
Most Managed WordPress hosts completely isolate websites and therefore provide better security to avoid possible infection of multiple websites on a shared hosting account.
Some shared hosting has done this for their customers — e.g. like SiteGround for their shared hosting packages with new Site Tools, instead of the old cPanel.
So, our recommendation would be: separate sites and put all important/business related sites into their own (isolated) hosting accounts, if at all possible.
Article by Ivica Delic,
exclusively for Virusdie.
Join our private Facebook group to get help from other security experts, and share your own web security experiences and expertise. Group members receive exclusive news and offers. They can also communicate directly with the Virusdie team. Join us on Facebook.

Comments